Different Raid Levels Explained in Linux
Other more niche levels include RAID 6 10 and 51. It supports the creation of nested and non-standard RAID arrays.
Raid Level 0 1 5 6 And 10 Advantage Disadvantage Use
The most commonly levels are RAID 0 1 5 6 and 10.

. Which one is recommended for file server and database. RAID 6 striping with double parity. Linux MD RAID 10.
Different RAID levels. The different ways in which data is spread out across the drives in. But most organizations use one of five namely RAID 0156 or 10.
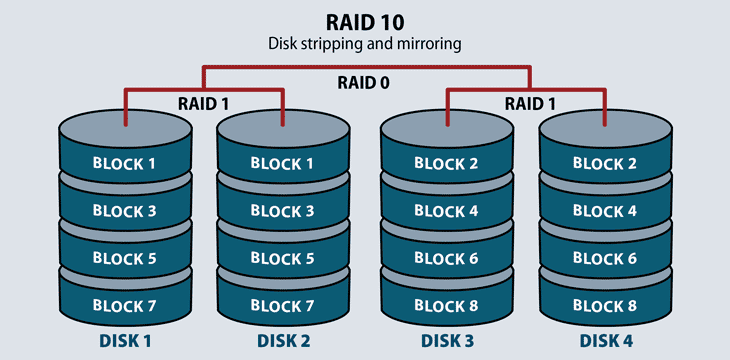
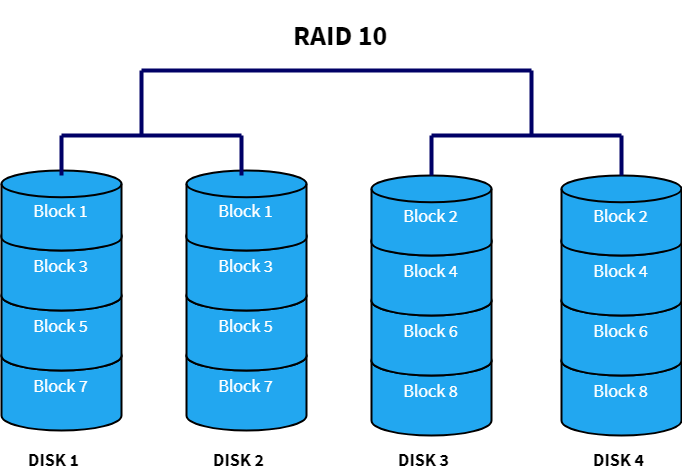
RAID 10 also known as RAID 10 This article explains the main difference between these raid levels along with an easy to understand diagram. It uses the mirroring technique. In the figure blocks 0123 form a stripe.
This level can survive multiple simultaneous drive failures. Mission critical system still. 5 rows QWhat are the different RAID levels.
RAID 01 is often interchanged for RAID 10. You can get about 95 of the performance of the RAID-0 with same amount of drives. The software to perform the RAID-functionality and control the drives can either be located on a separate controller card a hardware RAID controller or it can simply be a driver.
RAID is available in many different levels. Larger size and higher speed than RAID-1 and more redundancy than RAID-0. Similar to RAID 5.
RAID can be implemented in software or hardware and the Linux Operating systems support RAID out of the box as does pretty much every other operating system. RAID 1 mirroring. Large size fast speed and redundancy.
It does not support all RAID levels and is not so flexible as depends upon the operating system. The following list explains the standard RAID levels 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 and popular non-standard and hybrid options RAID 10. RAID 10 combining mirroring and striping.
In all the diagrams mentioned below. RAID 0 splits data across any number of disks allowing higher data throughput. There is no arrangement in case data is lost.
Striped set of Mirrored Subset. Whether hardware or software RAID is available in different schemes or RAID levels. Therefore you can choose between hardware RAID software RAID and firmware RAID.
RAID 0 1 and 5 work on both HDD and SSD media. Linux software RAID can also support standard RAID 0 RAID 1 RAID 4 RAID 5 and RAID 6 configurations. 11 rows An obsolete implementation of striping similar to RAID 0 it stripes at the bit level instead of by blocks.
Four or more drives are made into two mirrors that are striped. There are many different levels of RAID the most common being RAID 0 RAID 1 and RAID 5. A B C D E and F represents blocks.
RAID-0 Stripping Blocks are stripped across disks. The distribution of data across multiple drives can manage either by computer hardware or by software. RAID10 Combine of Mirror Stripe.
RAID6 Double Disk Distributed Parity. RAID works by storing the data on multiple disks and allows inputoutput ie. Let us get a.
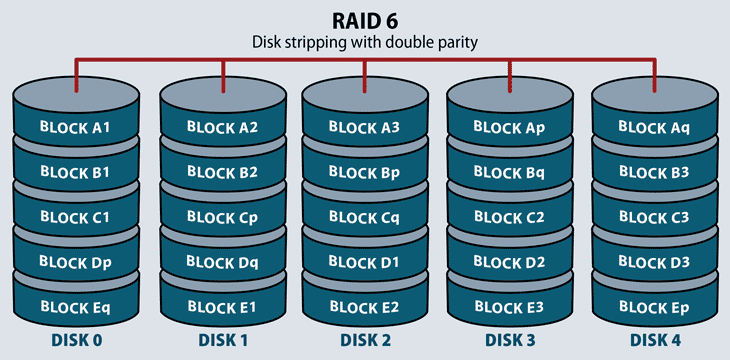
All RAID levels involve storing data across multiple drives but the exact method of doing so varies widely. RAID 6 is upgraded version of RAID 5 where it has two distributed parity which provides fault tolerance even after two drives fails. Here we will see only the RAID Levels which is used mostly in real environment.
The total array size is reduced by parity. RAIDs are in various Levels. Instead of placing just one block into a disk at a time we can work with two or more blocks placed into a disk before moving on to the next one.
The Linux kernel provides this level. A single drive failure will rebuild. RAID in Linux works in multiple ways configurations called as Levels such as Concatenated Linear Disk Striping RAID Level 0 Disk Mirroring RAID Level 1 Disk Parity RAID Level 4 Disk Redundant RAID Level 5 etc.
Standard RAID levels. In the next article. This RAID level is often referred to as striping and has the benefit of increased performance.
Each level also has very different pros and cons. RAID levels 4 and 6 also work on both media but are rarely seen in practice. An individual file is read from multiple disks giving it access to the speed and capacity of all of them.
Additionally you can choose how to implement RAID on your system. RAID-10 is an in-kernel combination of RAID-1 and RAID-0 that is more efficient than simply layering RAID levels. RAID 7 is a proprietary level of RAID owned by the now-defunct Storage Computer Corporation.
RAID 10 RAID 10 This level performs Mirroring of data prior stripping which makes it much more efficient and redundant as compared to RAID 01. The most common types are RAID 0 RAID 1 and its variants RAID 5 and RAID 6. This can be used in organizations where high performance and security are required.
RAID5 Single Disk Distributed Parity. Different types of RAID levels. Setup RAID Level 6 Striping with Double Distributed Parity in Linux Part 5.
RAID-10 has a layout far which can provide sequential read throughput that scales by number of drives rather than number of RAID-1 pairs. Working with RAID in Linux. RAID 0 Disk striping.
It utilizes full storage capacity. Its limitation is that it cannot service multiple requests. On most situations you will be using one of the following four levels of RAIDs.
Data is simply striped across multiple disks for parallel storage and retrieval. Here is a list of the most used RAID levels. The various types of RAID levels are as follows.
In computer storage the standard RAID levels comprise a basic set of RAID configurations that employ the techniques of striping mirroring or parity to create large reliable data stores from multiple general-purpose computer hard disk drives. These were the two different types of RAID implementation and we will discuss about different RAID levels like RAID 0 RAID 1 RAID 5 etc. RAID 5 striping with parity.
A rare implementation of parity striping. Nested RAID RAID are managed using mdadm package in most of the Linux distributions. Multiple RAID levels can also be combined or nested for.
A rare implementation of parity striping at the block level with an entire disk dedicated to parity data.

Raid 2 Raid 3 Raid 4 Raid 6 Explained With Diagram

Raid Level 0 1 5 6 And 10 Advantage Disadvantage Use

Raid Level 0 1 5 6 And 10 Advantage Disadvantage Use

Raid Descriptions With Diagrams Wow Raid Nas Backup Coding

Raid 5 Example Comptia A Data Recovery Raid
Types Of Raid Arrays Here Is All You Need To Know Hackanons

Raid Level 0 1 5 6 And 10 Advantage Disadvantage Use

Raid Level Explained Raid 2 Raid 3 Raid 4 Raid 6
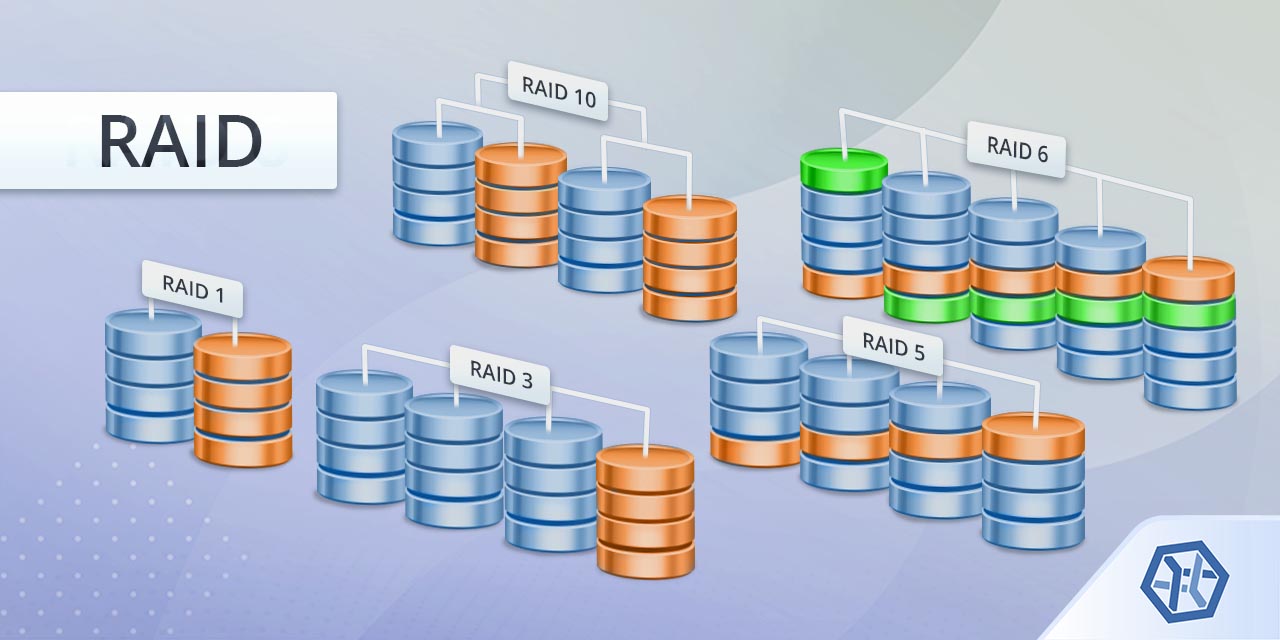
The Fundamentals Of Raid Storage Technology
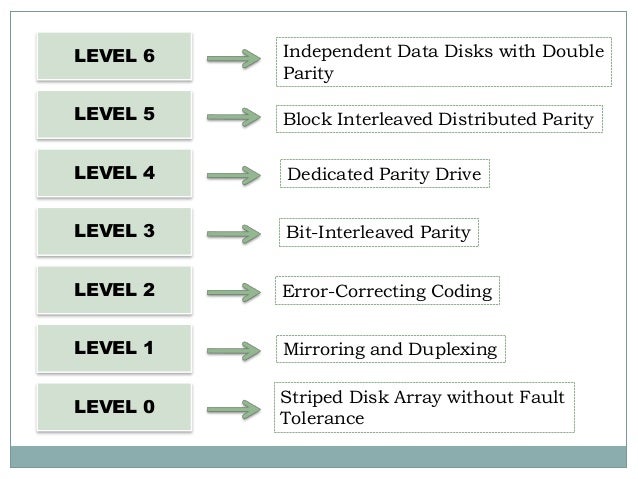
Hard Drive Raid Levels Explained Technology News And Information By Seniordba
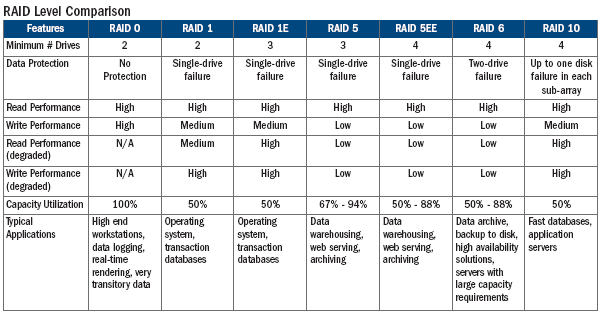
Raid Site Reliability Engineer Handbook

Raid Levels 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 1 0 Features Explained In Detail Golinuxhub
Raid Levels Explained Enterprise Storage Forum
Raid Levels Explained Enterprise Storage Forum

Raid Levels 0 1 4 5 6 10 Explained Boolean World

Introduction To Raid Concepts Of Raid And Raid Levels Part 1


Comments
Post a Comment